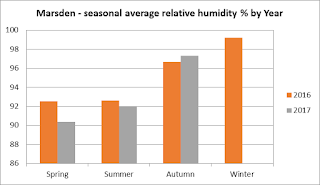
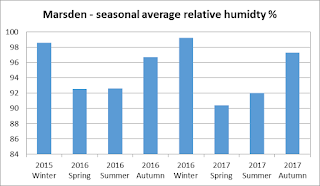
A new week and a new site - let's take a look up north at Marsden. The following graphs show how the relative humidity (level of moisture in the air) changes at this site month to month and across the seasons.
Thanks again to Andy Burn for the graphs and to all our Marsden volunteers who collected the data!
Showing posts with label weather. Show all posts
Showing posts with label weather. Show all posts
Tuesday, 27 November 2018
Thursday, 25 October 2018
Environmental monitoring results: Chatsworth data
One of our newest environmental monitoring sites is Chatsworth. Set up last year, our volunteers have been collecting temperature, humidity, and water table depth data. As it's too soon to compare yearly or seasonal data, let's have a look at these three variables together.
Thanks again to Andy Burn for producing these graphs. We look forward to seeing how this year's data compares.
Thanks again to Andy Burn for producing these graphs. We look forward to seeing how this year's data compares.
Tuesday, 9 October 2018
Environmental monitoring results: Holme humidity
In our last post we showed the temperature variation at Holme Moss and how this changes monthly and across the seasons. Another variable that our volunteers measure on site is the relative humidity (level of moisture in the air). The following graphs show how this varies monthly, yearly, and seasonally.
Special thanks to Andy Burn for producing these graphs.
Special thanks to Andy Burn for producing these graphs.
Tuesday, 2 October 2018
Environmental monitoring results: Holme temperature
As the temperature starts to drop outside this week, let's have a look at the temperature results from Holme Moss. This environmental monitoring site is situated at about 540m above sea level.
Thanks again to Andy Burn for producing these graphs which show the monthly and seasonal average (mean) air temperatures collected over the last three years by our volunteers.
Thanks again to Andy Burn for producing these graphs which show the monthly and seasonal average (mean) air temperatures collected over the last three years by our volunteers.
Friday, 16 December 2016
Storm Angus
The UK was battered by rain and high winds in November this year as a storm named 'Angus' made an appearance.
Angus hit the
south of England during the 19th and 20th
of November, but it wasn't until the day after when the heavy rains had moved north and reached the Peak District and South Pennines, that we were able to record the storm.
This blog post looks at how the equipment installed on our Community Science environmental monitoring sites reacted to this event.
Volunteers collect information from these sites each month, and use the same equipment and methods as Moors for the Future science team do on other sites where conservation works have taken place. In this case though, we're interested in capturing long-term climate datasets on sites where conservation works haven't taken place.
The bar chart below shows how much rain fell on each of our five sites over four days:
 |
| Click on the image to see a larger version |
Marsden had the most consistent rainfall with 71.2 mm
recorded across the four days. Despite Holme only recording rainfall on
the second couple of days of the storm (21st and 22nd), it received the second highest amount, with 73 mm in total. The Roaches had
45.6 mm over the four days and Edale had a surprisingly small 33.6 mm. Out in front was Burbage Moor, which recorded a total of 78mm over the 4 days, with nearly 70% of this falling on Monday 21st.
So how did all this water behave once it reached the ground? The line graph below shows how the water table on the
sites changed over the days around the storm. The 'zero' mark on the left hand axis represents ground level, and each line shows how close to the surface the water was (in metres) over the four days of the 'official' storm, and a couple of days afterwards.
 |
| Click on the image to see a larger version |
We can't be certain what is happening here, but from a quick look at the graph we could surmise that despite having less rainfall than
the other sites the water table at Edale (the driest of the sites) increased the most, jumping up by around
10 cm, before rapidly decreasing again as water drained away.
The Roaches water table also had a sharp increase, however as the water on the site is consistently close to the surface, it only increased to around ground level - but then seemed to stay
there, possibly because the site has plenty of Sphagnum moss, and clay underlying the peat layer.
On the Holme site the water was also already close to the surface, and despite having very high
rainfall, the water table didn’t change dramatically, or as quickly.
Marsden did show an increase in water table - but it was gradual and the new
higher level was maintained in the days after the storm event. The site is very flat and also contains Sphagnum moss among its vegetation, which could perhaps help to explain this pattern.
The site which had the most rainfall (Burbage) also showed a small response - the water was almost at surface level; and you can see it even exceeds zero, forming a puddle! This is another very flat site and does have some Sphagnum moss present.
The complexity of hydrological data - taking into account the many variables which can affect the way water behaves on a site - means that we cannot draw any firm conclusions just yet. However, our volunteers will be analysing our environmental data in more depth in the near future...
Graphs and text by volunteer Mollie Hunt, and the CSP team....
Friday, 25 November 2016
Top tips for entering our photography competition
Here are 6 top tips for those thinking of entering our 'Water in the Uplands' photo competition: http://www.moorsforthefuture.org.uk/community-science/competition
1. Slow the flow
Reduce your camera’s shutter speed to catch the dreamy effect of water in flow.
A tripod is a handy piece of kit to keep your camera steady, but alternatively use a small bean bag or even a folded up jumper to sit your camera on.
Use the self-timer function so you can go hands free, ensuring the camera doesn’t move while it’s recording the shot.
2. Beauty in the details
 Look more closely at water and you’ll be amazed by some of the little details to be found.
Look more closely at water and you’ll be amazed by some of the little details to be found.
Capture bubbles below a waterfall, reflections in puddles and get really close to discover the world of water droplets.
3. Water in the landscape
 Consider the wider landscape and make water a part of the bigger picture.
Consider the wider landscape and make water a part of the bigger picture.
Think how it has shaped its surroundings whether naturally or by the addition of man-made structures like bridges and weirs.
4. Go abstract
There’s so much potential for creating abstract images of water.
Create patterns from a flowing waterfall or focus on ripples in a calm pool.
5. Winter wonderland
 Winter is a great time to photograph water as the cold takes hold to create ice and snow.
Winter is a great time to photograph water as the cold takes hold to create ice and snow.
Get out early after a cold night and capture incredible ice formations clinging to plants and rocks.
Alternatively take a break from sledging after a big snowfall and capture incredible winter scenery.
6. Life giving water
There are many plant and animal species that rely on the habitats provided by the water in our uplands.
Capture beautiful creatures in their watery homes or look at plants like Sphagnum mosses that keep our blanket bogs saturated.
Tom Aspinall
1. Slow the flow
Reduce your camera’s shutter speed to catch the dreamy effect of water in flow.
A tripod is a handy piece of kit to keep your camera steady, but alternatively use a small bean bag or even a folded up jumper to sit your camera on.
Use the self-timer function so you can go hands free, ensuring the camera doesn’t move while it’s recording the shot.
2. Beauty in the details
 Look more closely at water and you’ll be amazed by some of the little details to be found.
Look more closely at water and you’ll be amazed by some of the little details to be found.Capture bubbles below a waterfall, reflections in puddles and get really close to discover the world of water droplets.
3. Water in the landscape
 Consider the wider landscape and make water a part of the bigger picture.
Consider the wider landscape and make water a part of the bigger picture.Think how it has shaped its surroundings whether naturally or by the addition of man-made structures like bridges and weirs.
4. Go abstract
There’s so much potential for creating abstract images of water.
Create patterns from a flowing waterfall or focus on ripples in a calm pool.
5. Winter wonderland
 Winter is a great time to photograph water as the cold takes hold to create ice and snow.
Winter is a great time to photograph water as the cold takes hold to create ice and snow.Get out early after a cold night and capture incredible ice formations clinging to plants and rocks.
Alternatively take a break from sledging after a big snowfall and capture incredible winter scenery.
6. Life giving water
There are many plant and animal species that rely on the habitats provided by the water in our uplands.
Capture beautiful creatures in their watery homes or look at plants like Sphagnum mosses that keep our blanket bogs saturated.
Tom Aspinall
Labels:
autumn,
beautiful,
bog,
climate,
cloud,
competition,
environmental,
filming,
hydrology,
microscope,
national park,
nature,
photo,
photography,
weather,
wildlife
Tuesday, 1 November 2016
Autumn cloud inversions
Autumn is a fantastic time of year to witness some stunning scenery and landscapes - and perhaps one of the very best sights is a cloud inversion:
Above is the view of Edale valley from Mam Nick yesterday. Inversions like this need specific conditions to form. They are most likely to be seen in early morning when a layer of saturated cold air becomes trapped underneath a layer of warmer air higher up the valley sides.
The inversion was still visible from Kinder Scout later yesterday morning as Community Science volunteers headed to the Environmental Monitoring site:
From the plateau cloud could be seen still clinging to the Hope Valley in the middle distance; while the crystal clear upper layers of air allowed a stunning view for miles:
Above is the view of Edale valley from Mam Nick yesterday. Inversions like this need specific conditions to form. They are most likely to be seen in early morning when a layer of saturated cold air becomes trapped underneath a layer of warmer air higher up the valley sides.
The inversion was still visible from Kinder Scout later yesterday morning as Community Science volunteers headed to the Environmental Monitoring site:
 |
| Looking back towards Edale - Rob Westrick |
 |
| Remnants of cloud still visible in Edale from higher up the hill - Rob Westrick |
 |
| View from Kinder - Richard Walker |
Monday, 17 October 2016
Photo competition 2016 - 'Water in the Uplands'
We're very happy to announce that this year's Community Science photo competition is now open for entries.
The theme for entries this year is 'WATER IN THE UPLANDS' - intended in part to draw attention to the wide-ranging positive effects of re-wetting blanket bogs. As ever you are free to interpret this theme as you see fit - using as much creativity and imagination as possible!
This year there are age-based categories for photographers to enter - 'Adults' or '15 and under', and we have kindly been donated some fantastic prizes:
The deadline for entries is 31st Dec 2016. For full details of how to enter, please see our webpage. Good luck!
The theme for entries this year is 'WATER IN THE UPLANDS' - intended in part to draw attention to the wide-ranging positive effects of re-wetting blanket bogs. As ever you are free to interpret this theme as you see fit - using as much creativity and imagination as possible!
This year there are age-based categories for photographers to enter - 'Adults' or '15 and under', and we have kindly been donated some fantastic prizes:
 |
| The winner of the adults category will win this amazing HD nest box camera system worth £99 - donated by Gardenature. |
 |
| The winner of the 15 and under category will win this (appropriately) waterproof camera worth £130 donated by Harrison Cameras. |
Labels:
blanket,
bog,
climate,
competition,
conservation,
environmental,
kate,
moor,
moorland,
moors,
nature,
photo,
photography,
rainfall,
water,
weather
Wednesday, 20 January 2016
The wettest month ever
One of the variables which is recorded on each Community Science Environmental Monitoring site in rainfall level.
To do this, volunteers install an automated rain gauge. This works by channeling water which falls on the surface of a bucket down a funnel into a tipper mechanism. Each time the tipper fills, an automatic logger records 1 'event'. Each event (i.e. tip) equates to 0.2mm of rain, so if you know how many times the tipper has tipped you can work out how much rain has fallen and when.
As you may know, December 2015 holds the overall UK prize for the wettest month since records began. So how much rain did we record?
The graph below shows the daily amount of rain that fell on our site near Holme (West Yorkshire) throughout December - downloaded from the rain gauge by the volunteers who look after the site.
The wettest days were the 12th and the 26th - both recording over 50mm of rain - and as you might remember the heavy rainfall around both storms 'Desmond' and 'Eva' (Boxing day) caused extensive flooding in areas of Cumbria,Yorkshire and Lancashire - and equate to these readings.
The total which fell on this site in December was 294.8mm, this compares to 230mm which was the average UK total for the month, and 137mm which was the figure for England. More information about December's weather can be found on the Met Office website.
To do this, volunteers install an automated rain gauge. This works by channeling water which falls on the surface of a bucket down a funnel into a tipper mechanism. Each time the tipper fills, an automatic logger records 1 'event'. Each event (i.e. tip) equates to 0.2mm of rain, so if you know how many times the tipper has tipped you can work out how much rain has fallen and when.
 |
| Inside the rain gauge - the tipper mechanism is visible in the middle |
As you may know, December 2015 holds the overall UK prize for the wettest month since records began. So how much rain did we record?
The graph below shows the daily amount of rain that fell on our site near Holme (West Yorkshire) throughout December - downloaded from the rain gauge by the volunteers who look after the site.
The wettest days were the 12th and the 26th - both recording over 50mm of rain - and as you might remember the heavy rainfall around both storms 'Desmond' and 'Eva' (Boxing day) caused extensive flooding in areas of Cumbria,Yorkshire and Lancashire - and equate to these readings.
 | ||
| December rainfall at Holme EM site (mm) |
The total which fell on this site in December was 294.8mm, this compares to 230mm which was the average UK total for the month, and 137mm which was the figure for England. More information about December's weather can be found on the Met Office website.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)